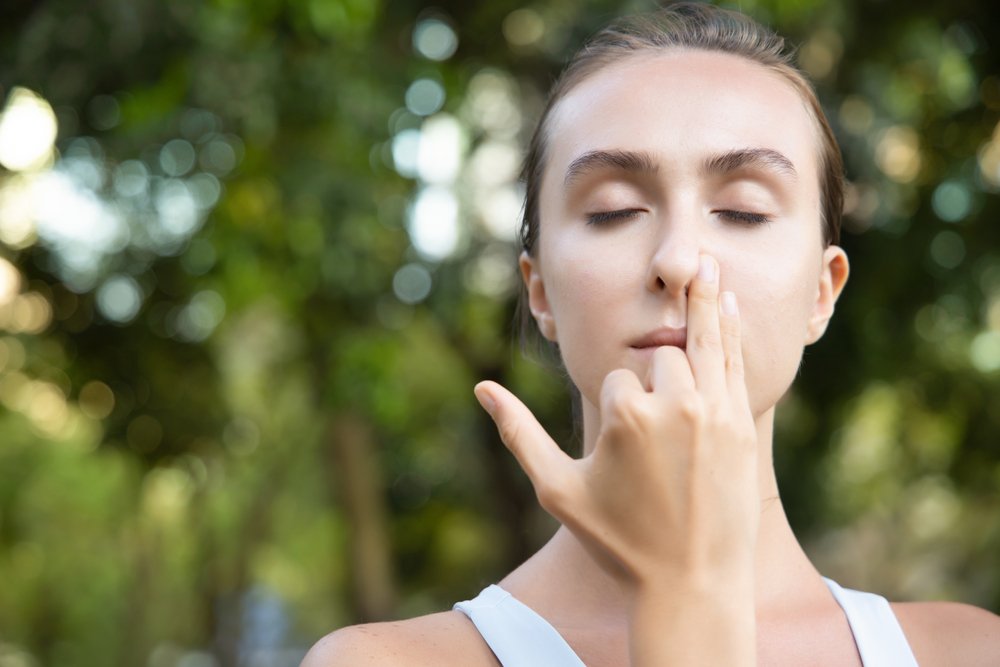
What is the breathwork practice ? Definition and technics

In our fast-paced world, where stress and anxiety have become unwelcome companions, the ancient practice of breathwork is experiencing a renaissance. This powerful tool for physical and mental well-being has been gaining traction among wellness enthusiasts and healthcare professionals alike. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fascinating world of breathwork, its various techniques, and the myriad benefits it offers for our overall health.

What is Breathwork?
Breathwork is a term that encompasses a wide range of breathing exercises and techniques designed to improve physical, mental, and emotional well-being. At its core, breathwork involves consciously changing your breathing pattern to influence various aspects of your health. This ancient practice has roots in many cultures and traditions, including yoga, meditation, and various spiritual practices.
The fundamental principle behind breathwork is that by controlling our breath, we can influence our autonomic nervous system, which regulates many of our body’s involuntary functions. This includes our heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and stress response. By manipulating our breathing, we can potentially shift our body from a state of stress (sympathetic nervous system activation) to a state of relaxation (parasympathetic nervous system activation).

Types of Breathwork
There are numerous breathwork techniques, each with its own specific focus and benefits. Here are some of the most popular and well-researched methods:
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing or abdominal breathing, is a fundamental technique that forms the basis of many other breathwork practices. This method involves breathing deeply into the abdomen rather than shallowly into the chest.
How to practice:
1. Lie down or sit comfortably with one hand on your chest and the other on your belly.
2. Breathe in slowly through your nose, allowing your belly to expand while keeping your chest relatively still.
3. Exhale slowly through your mouth, feeling your belly fall.
4. Repeat for 5-10 minutes.

2. Box Breathing
Box breathing, also called square breathing, is a simple yet effective technique often used by athletes, military personnel, and those seeking stress relief.
How to practice:
1. Inhale slowly for a count of 4.
2. Hold your breath for a count of 4.
3. Exhale slowly for a count of 4.
4. Hold your breath for a count of 4.
5. Repeat the cycle for 5-10 minutes.

3. Alternate Nostril Breathing
This technique, derived from yoga practices, is believed to balance the left and right hemispheres of the brain and promote relaxation.
How to practice:
1. Sit comfortably with your left hand on your lap and your right hand near your nose.
2. Use your right thumb to close your right nostril and inhale through your left nostril.
3. Close your left nostril with your ring finger, release your thumb, and exhale through your right nostril.
4. Inhale through your right nostril, then close it.
5. Exhale through your left nostril and repeat the cycle for 5-10 minutes.

4. 4-7-8 Breathing Technique
Developed by Dr. Andrew Weil, this technique is often referred to as a “natural tranquilizer for the nervous system.”
How to practice:
1. Exhale completely through your mouth.
2. Close your mouth and inhale quietly through your nose for a count of 4.
3. Hold your breath for a count of 7.
4. Exhale completely through your mouth for a count of 8.
5. Repeat the cycle for a total of four breaths.

5. Holotropic Breathwork
Holotropic breathwork is a more intense form of breathwork that aims to induce altered states of consciousness for therapeutic purposes. This technique should only be practiced under the guidance of a trained facilitator.
How it works:
Participants lie down and engage in rapid, deep breathing for extended periods (usually 2-3 hours). This is often accompanied by evocative music and followed by a period of integration and sharing.

The Science Behind Breathwork
Recent studies have shed light on the physiological mechanisms behind the benefits of breathwork. When we engage in deep, slow breathing exercises, we activate the parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
This activation leads to a cascade of physiological changes:
1. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Increase: HRV is a measure of the variation in time between each heartbeat. Higher HRV is associated with better cardiovascular health and stress resilience.
2. Cortisol Reduction: Deep breathing has been shown to lower cortisol levels, the primary stress hormone in our body.
3. Improved Oxygen Exchange: Proper breathing techniques can enhance the efficiency of oxygen exchange in the lungs, potentially benefiting those with respiratory conditions.
4. Enhanced Brain Function: Studies have shown that certain breathwork practices can increase alpha brain wave activity, associated with relaxation and improved cognitive function.
5. Immune System Boost: Regular breathwork practice has been linked to improvements in immune function, possibly due to its stress-reducing effects.
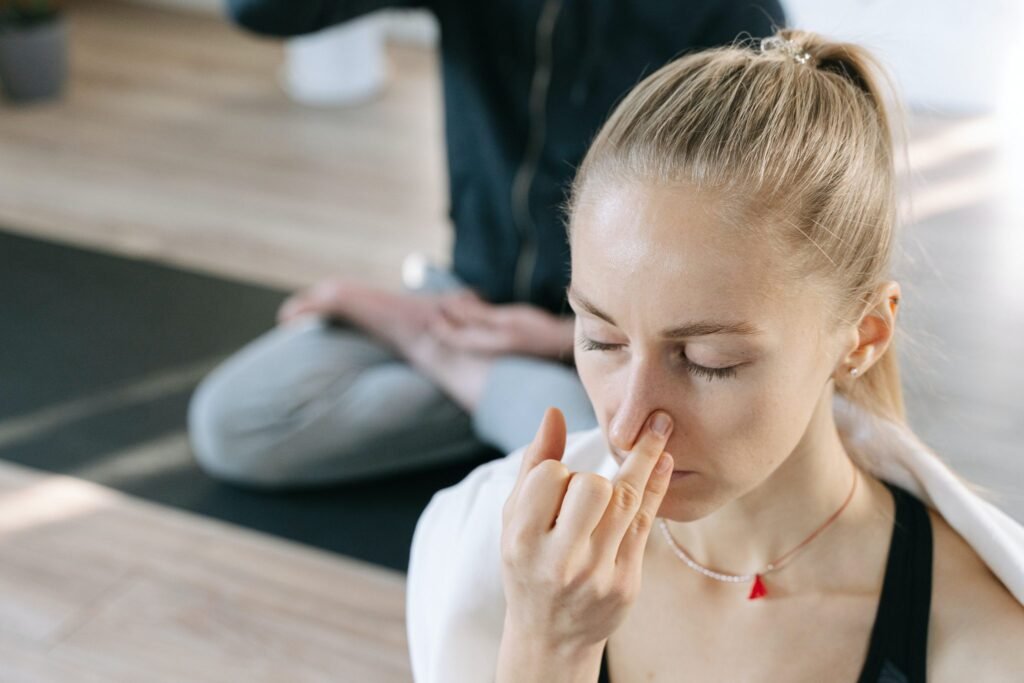

Benefits of Breathwork
The practice of breathwork offers a wide array of benefits for both physical and mental health:
Physical Health Benefits
1. Lower Blood Pressure: Regular breathwork practice has been shown to significantly reduce blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
2. Improved Lung Function: Breathwork exercises can increase lung capacity and improve overall respiratory function, potentially benefiting those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma.
3. Enhanced Cardiovascular Health: By improving heart rate variability and reducing stress, breathwork can contribute to better heart health.
4. Pain Management: Some studies suggest that certain breathwork techniques can help manage chronic pain conditions by altering pain perception and reducing stress.
5. Better Sleep: Relaxation-inducing breathwork practices can improve sleep quality and help combat insomnia.

Mental Health Benefits
1. Stress Reduction: Perhaps the most well-known benefit of breathwork is its ability to activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress and anxiety.
2. Improved Mood: Regular breathwork practice has been associated with reductions in symptoms of depression and overall improvements in mood.
3. Enhanced Focus and Concentration: By promoting a state of calm alertness, breathwork can improve cognitive function and mental clarity.
4. Emotional Regulation: Breathwork can help individuals better manage negative emotions and develop greater emotional resilience.
5. Mindfulness and Present Moment Awareness: Many breathwork techniques incorporate elements of mindfulness, helping practitioners cultivate greater awareness of the present moment.

Incorporating Breathwork into Your Daily Routine
To reap the full benefits of breathwork, consistency is key. Here are some tips for making breathwork a part of your daily life:
1. Start Small: Begin with just 5 minutes of practice per day and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable.
2. Choose a Consistent Time: Whether it’s first thing in the morning, during your lunch break, or before bed, pick a time that works for you and stick to it.
3. Experiment with Different Techniques: Try various breathwork methods to find what resonates best with you.
4. Use Technology: There are numerous apps and online resources that can guide you through breathwork exercises.
5. Combine with Other Practices: Incorporate breathwork into your yoga or meditation practice for enhanced benefits.
6. Practice in Different Settings: While a quiet space is ideal, learning to practice breathwork in various environments can help you use it effectively in stressful situations.

Precautions and Considerations
While breathwork is generally safe for most people, there are some important considerations:
✔ Medical Conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart problems, or respiratory issues, should consult with a healthcare provider before starting a breathwork practice.
✔ Pregnancy: Pregnant women should avoid certain intense breathwork techniques and consult with their healthcare provider.
✔ Dizziness or Lightheadedness: If you experience these symptoms during practice, return to normal breathing and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
✔ Mental Health Conditions: Those with severe mental health conditions should practice breathwork under the guidance of a mental health professional.

Pranayama Breathwork: A Comprehensive Overview
Definition and Origins
Common Pranayama Techniques
1. Dirga Pranayama (Three Part Breath): This technique involves breathing into three parts of the abdomen: the belly, rib cage, and chest. It’s ideal for beginners and helps in filling the lungs completely.
2. Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing): This practice involves breathing through alternate nostrils, believed to balance the mind, body, and soul. It’s associated with reduced anxiety and increased attention.
3. Ujjayi Pranayama (Ocean Breath): Ujjayi involves breathing through the nose with a slight constriction in the throat, creating a sound reminiscent of ocean waves. It’s often used in vinyasa yoga for its calming and focusing effects.
4. Bhramari Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath): This technique involves making a humming sound while exhaling, believed to calm the mind and body and increase concentration.
5. Kapalabhati Pranayama (Skull Shining Breath): Kapalabhati involves passive inhalations and forceful exhalations. It’s invigorating and is believed to help in detoxifying the body.
6. Anuloma Viloma (Alternate Nostril Breathing with Retention): Similar to Nadi Shodhana, this technique involves alternate nostril breathing but includes breath retention. It’s believed to help clear nasal passages and balance body energies.

Benefits of Pranayama
Mental Health Benefits
1. Anxiety and Stress Reduction: Multiple studies have demonstrated that regular pranayama practice can significantly reduce anxiety and stress levels. For instance, healthcare professionals practicing pranayama twice daily for 28 days showed reduced stress and anxiety scores.
2. Improved Sleep Quality: Pranayama has been shown to improve sleep quality by decreasing sleep disturbances and daytime sleepiness.
3. Enhanced Mood and Well-being: Studies have associated pranayama with improved mood and overall well-being, including in chemotherapy patients and healthcare workers.

Physical Health Benefits
1. Cardiovascular Health: Pranayama may have beneficial effects on heart function and has been shown to reduce the risk of arrhythmia.
2. Respiratory Function: Studies have demonstrated that pranayama can improve lung capacity and breath-holding capacity.
3. Neurological Benefits: Pranayama has been linked to improved brain activities, attention, and awareness.
Scientific Backing
1. A comprehensive review supports the integration of pranayama for overall health improvements, urging further research to unravel specific benefits.
2. A quasi-randomized clinical trial highlighted improvements in perceived stress, well-being, and quality of life through a specially designed pranayama protocol.
3. Studies on healthcare professionals and chemotherapy patients have shown positive effects on mental health, sleep quality, and overall well-being.

Safety Considerations
1. Physical Strain: Improper technique can lead to muscle strains and sprains, particularly in vigorous breathing exercises.
2. Hyperventilation: Some techniques, like bhastrika, can lead to hyperventilation if not done under proper guidance.
3. Medical Conditions: Individuals with specific health conditions, such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, or psychiatric conditions, should avoid certain pranayama practices or consult with a healthcare provider before starting.
4. Expert Guidance: Beginners should practice pranayama under the guidance of a qualified instructor to ensure proper technique and avoid potential risks.
5. Gradual Progression: It’s important to progress slowly and practice regularly, allowing the body to adapt to the breathing techniques without overexertion.
Comparison with Other Forms of Breathwork
Conclusion
Breathwork is a powerful tool for enhancing both physical and mental well-being. From reducing stress and anxiety to improving cardiovascular health and cognitive function, the benefits of this ancient practice are vast and well-documented. By incorporating various breathwork techniques into your daily routine, you can tap into the innate healing power of your own breath, fostering greater health, balance, and presence in your life.

As research in this field continues to grow, we are likely to uncover even more ways in which conscious breathing can positively impact our health. Whether you’re looking to manage stress, improve your physical health, or simply cultivate greater mindfulness in your daily life, breathwork offers a accessible, effective, and empowering path to wellness.Remember, the breath is always with you – a constant companion and a powerful ally in your journey towards optimal health and well-being. So take a
deep breath, and begin your breathwork journey today.


