5 Simple Meditation Techniques to Reduce Anxiety
In our fast-paced world where information overload and constant stress have become a common thread of daily life, finding effective ways to manage anxiety has never been more crucial. As a powerful tool for mental well-being, meditation has emerged from ancient practice to become a scientifically validated approach for managing various types of anxiety and promoting overall health.
The Science Behind Meditation and Anxiety

Before diving into specific techniques, it’s important to understand why meditation works. Scientific studies have shown that regular practice can reduce anxiety symptoms by up to 60%. Research from prestigious institutions has demonstrated that meditation can be as effective as certain medications in reducing anxiety symptoms, with clinical trials showing approximately 20% reduction in symptom severity.

The practice works by affecting both our nervous system and brain structure. When we meditate, we activate our body’s relaxation response, lowering our heart rate and reducing the stress response that often triggers feelings of anxiety. This simple act has profound implications for our physical and mental well-being.
Where Does Anxiety Come From?
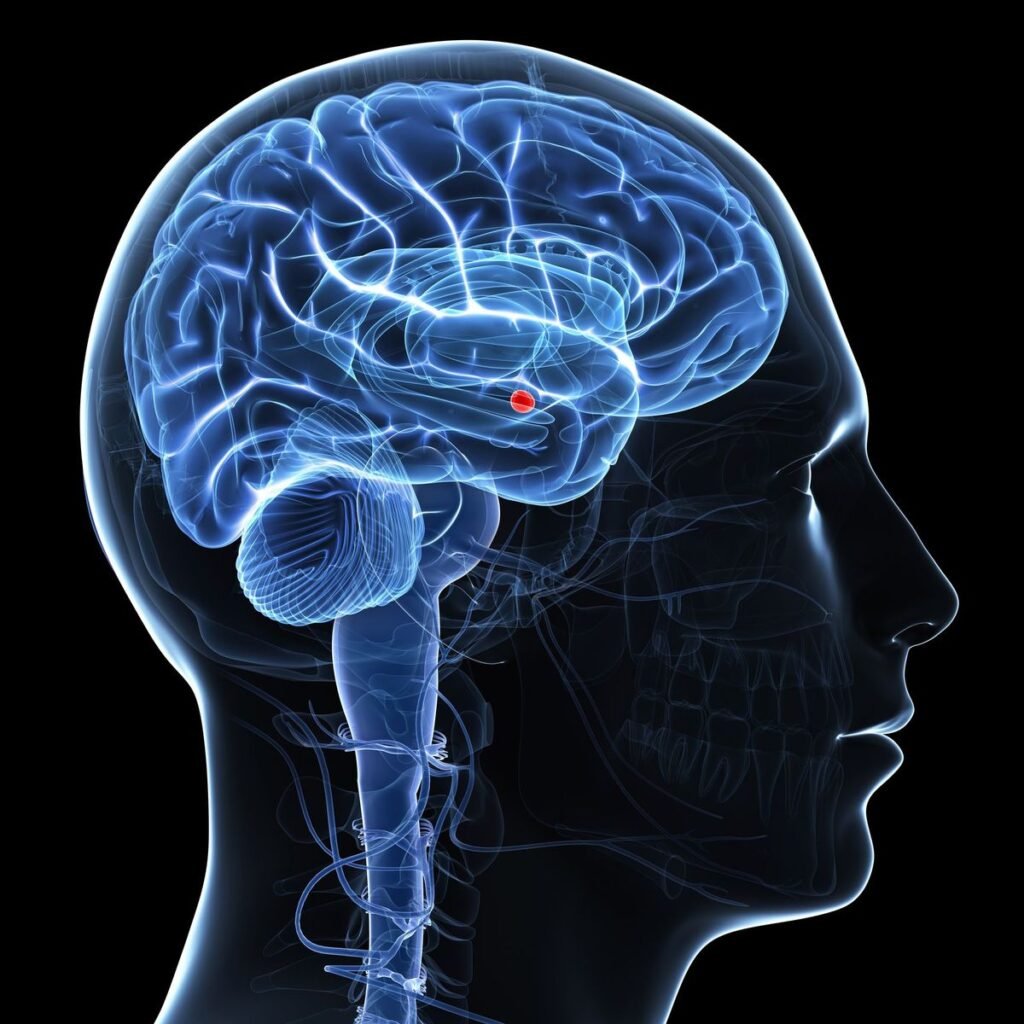
Anxiety emerges from a complex interplay of evolutionary, biological, and environmental factors. From an evolutionary perspective, anxiety developed as a crucial survival mechanism, helping our ancestors detect and respond to threats . This response is controlled by the brain’s limbic system, particularly the amygdala, which processes emotional stimulations.
5 Proven Meditation Techniques for Anxiety Management
1. Mindfulness Meditation
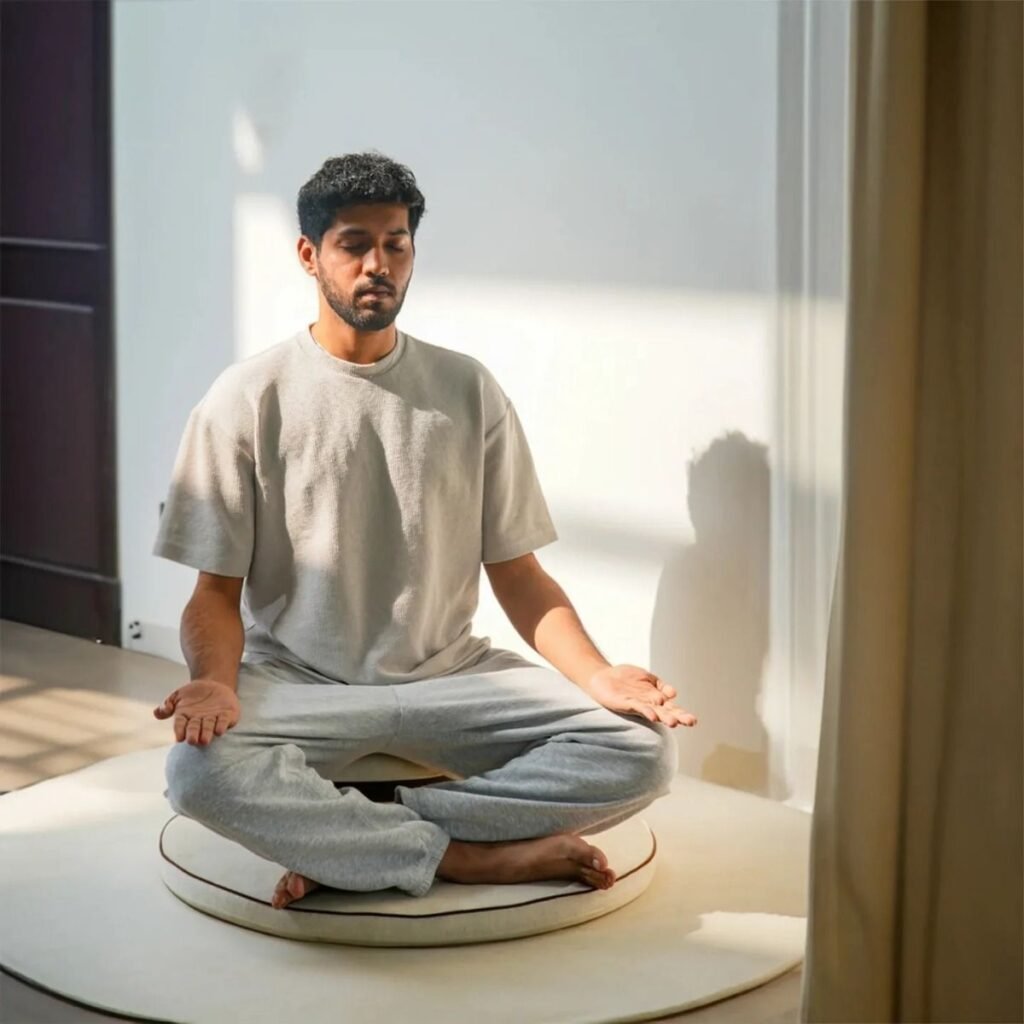

Mindfulness meditation, perhaps the most researched type of meditation, involves focusing on the present moment while observing your thoughts without judgment. When your mind wanders (as it naturally will), you simply return your attention to your point of focus.

Practical tip: Start with 5 minutes of mindful breathing. Find a quiet place and comfortable position. As you take deep breaths, notice the physical sensations and maintain mindful awareness of your breath. This basic human ability to focus can be developed through consistent practice.
Step-by-Step Guide to Practice
1. Setting Up Your Practice

- Choose a Quiet Space: Find a comfortable place where you won’t be disturbed
- Set a Time: Many meditation teachers recommend practicing in the morning before your to-do list takes over
- Get Comfortable: Sit in a position that’s comfortable but keeps you alert
- Start Small: Begin with 5-10 minutes and gradually increase duration as you become more comfortable
2. Basic Meditation Technique
Focus on Breath:

- Take deep breaths
- Notice the sensation of breathing
- Pay attention to how your body moves with each breath
- Use your breath as an anchor to the present moment
Body Awareness:
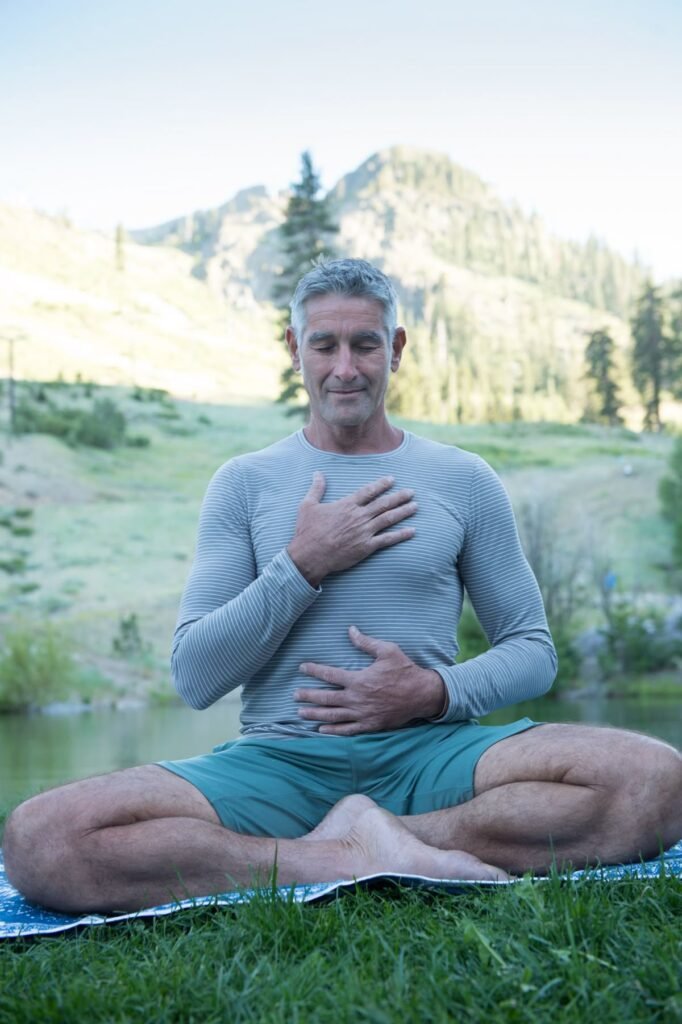

- Notice your posture
- Feel the weight of your body
- Be aware of physical sensations
Mind Management:

- When your mind wanders (it will), gently return focus to your breath
- Don’t judge yourself for getting distracted
- Treat each return to focus as a successful moment of practice
Common Obstacles and Solutions
1. Difficulty Maintaining Focus

Solution: Acknowledge distractions without judgment and gently return focus to your breath
2. Physical Discomfort

Solution:
Adjust your posture
Use cushions for support
Try mindful walking instead of sitting meditation
3. Time Constraints

Solution: Integrate short mindfulness practices into your daily routine:
Practice during lunch breaks
Do mindful breathing while commuting
Use waiting time for quick meditation sessions
Tools and Resources to Support Your Practice
Meditation Apps:
- Headspace: Offers well-organized courses and guided meditations
- Calm: Provides various guided sessions for stress reduction
- Insight Timer: Free app with diverse meditation practices
Guided Sessions:
- UCLA Mindful App: Offers guidance in multiple languages
- Plum Village: Supports mindfulness through guided meditations
2. Body Scan Meditation
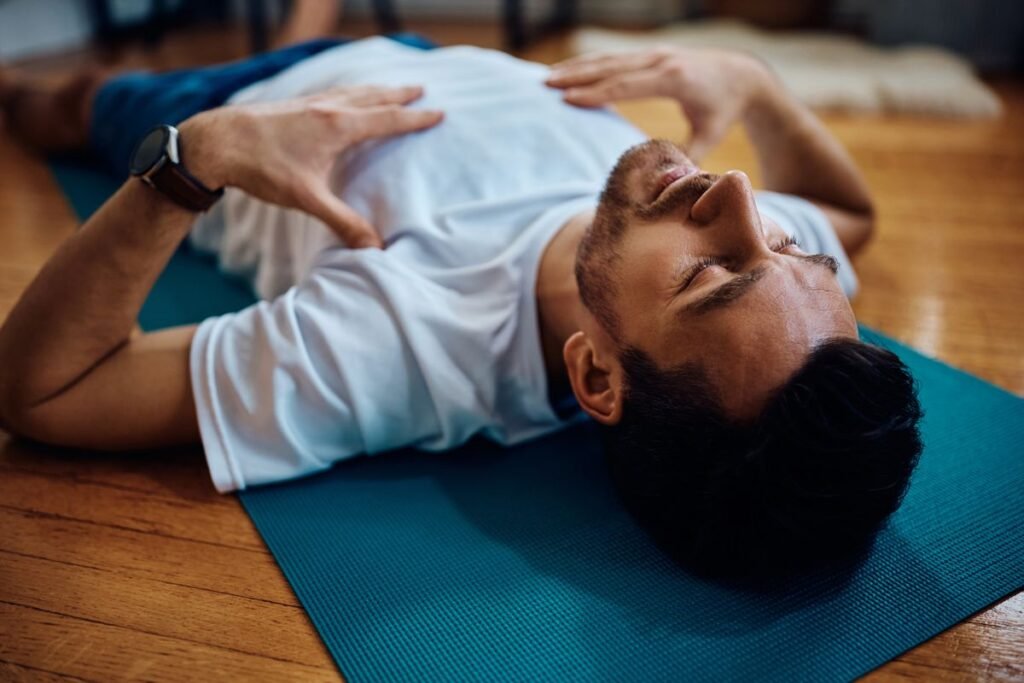

This form of meditation involves paying close attention to different parts of your body sequentially. It’s particularly effective for those who experience physical tension due to anxiety.
How to practice:
- Lie in a comfortable place
- Focus on each muscle group systematically
- Practice progressive muscle relaxation
- Notice any physical sensations without trying to change them
Step-by-Step Practice Guide
Preparation
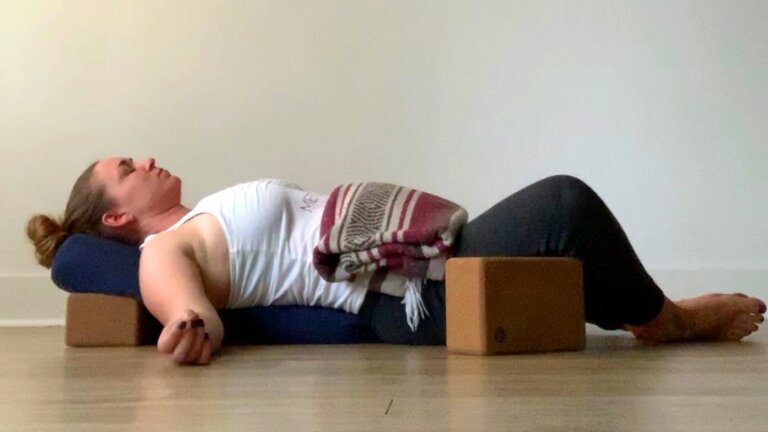

Find a Comfortable Position:
- Lie down on your back with arms at your sides and legs slightly apart
- Alternatively, sit comfortably in a chair with feet flat on the ground

Create the Right Environment:
- Choose a quiet space where you won’t be disturbed
- Ensure the temperature is comfortable
- Consider using a meditation cushion or mat for support
2. Basic Practice Steps

Begin with Breath Awareness:
- Take several deep breaths to center yourself
- Allow your breath to find its natural rhythm

Start the Systematic Scan:
- Begin at the top of your head
- Slowly move your attention downward through your body
- Notice any sensations without trying to change them
Scanning Sequence:

Focus on each area for a few moments:
- Forehead and facial muscles
- Neck and shoulders
- Arms and hands
- Chest and upper back
- Abdomen
- Hips and lower back
- Legs
- Feet and toes
Complete the Practice:
- Return attention to your breath
- Gradually become aware of your whole body
- Slowly open your eyes when ready
Variations and Adaptations
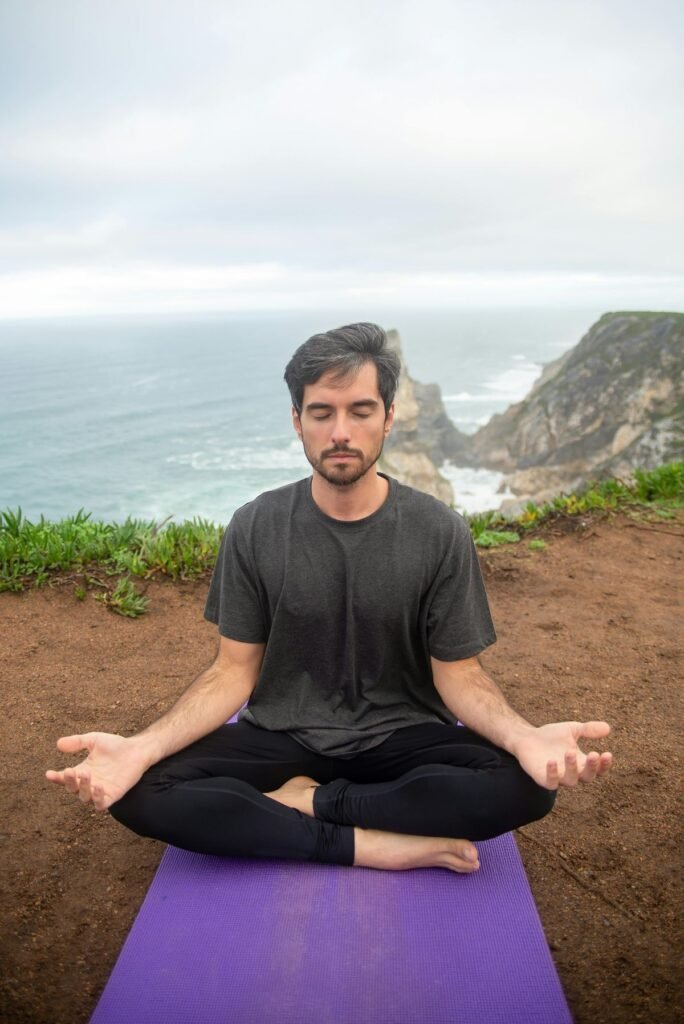

Different approaches are available to suit various needs:
- Interoception-Inspired Body Scan: Focuses on internal bodily sensations
- Mindfulness-Based Body Scan: Integrates mindfulness principles for mind-body synchronization
- Guided Body Scan for Beginners: Uses audio guidance for easier practice
- Body Scan for Stress Reduction: Emphasizes relaxation and tension release
3. Loving-Kindness Meditation
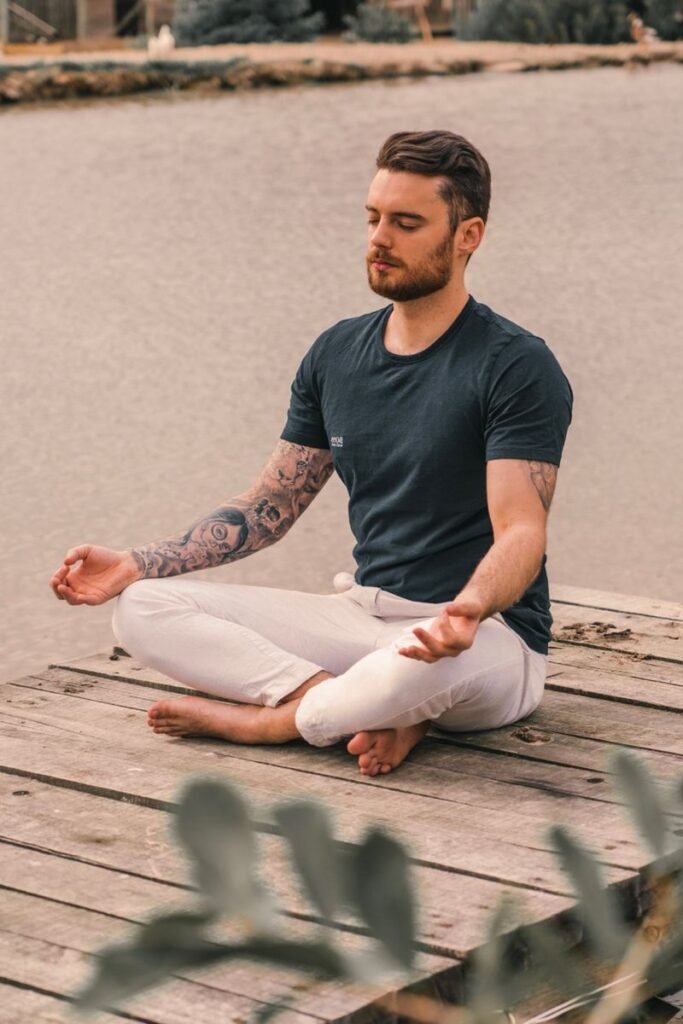

This meditation technique goes beyond typical relaxation practices by fostering positive emotions and reducing negative emotions. It’s particularly effective for those whose anxiety is connected to social situations or past events.
Key benefits:
- Reduces self-criticism
- Enhances emotional well-being
- Builds a supportive community mindset
- Improves mental clarity
Step-by-Step Practice Guide
Preparation

Find a Comfortable Position:
- Sit in a comfortable position, either on a chair or cushion
- Keep your back straight but not tense
Set Your Intention:
- Begin by setting an intention for your practice
- Focus on cultivating feelings of love and compassion
2. Basic Practice Steps

Start with Yourself:
Begin by directing loving-kindness towards yourself
Silently repeat phrases such as:”May I be happy””May I be healthy””May I be safe””May I live with ease”
Extend to Others (in this order):
- A loved one
- A neutral person
- A difficult person
- All beings
3. Common Phrases and Variations

You can use traditional phrases or create your own meaningful variations:
Extended Phrases:
“May you be held in loving-kindness”
“May you be happy and safe”
“May you be healthy in body and mind”
“May your heart know peace”
Overcoming Common Challenges

Feeling That Compassion is Limited:
- Remember that loving-kindness is an infinite resource
- Practice generosity in sending metta to all beings
Difficulty Feeling Genuine Compassion:
- Start with someone you naturally feel compassion for
- Gradually extend this feeling to others
Mind Wandering:
- Gently return attention to the practice when distracted
- Use the phrases as anchors for focus
Integration into Daily Life

During Daily Activities:
- Incorporate loving-kindness while cooking or cleaning
- Practice mindful listening during conversations
Walking Meditation:
- Combine walking with loving-kindness phrases
- Direct good wishes to people you pass
Journaling:
- Keep a metta journal
- Write loving-kindness phrases and reflect on your practice
4. Breath Awareness Meditation

Breath awareness is a powerful yet simple meditation practice that can be incorporated into your daily routine. It’s an excellent starting point for beginners and a great place to return to when anxiety peaks.
Simple practice guide:
- Find a comfortable position
- Focus on your natural breath
- Notice when your mind wanders
- Gently return to breath awareness
- Practice for short time periods initially
Step-by-Step Practice Guide
1. Preparation
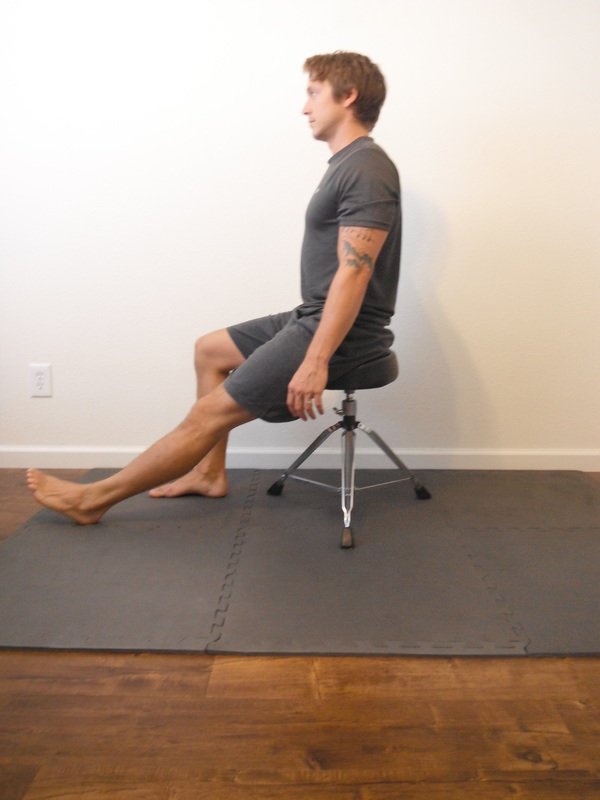
Find a Comfortable Position:
- Sit in a chair with feet flat on the floor
- Sit cross-legged
- Kneel in a comfortable position
- Ensure your position is stable and maintainable

Create the Right Environment:
- Choose a quiet space
- Set a time limit (5-10 minutes for beginners)
- Minimize potential distractions
2. Basic Practice Steps

Begin the Practice:
- Close your eyes or maintain a soft gaze
- Take a few deep breaths to center yourself
- Let your breath return to its natural rhythm

Focus on Your Breath:
- Pay attention to the sensation of breathing
- Notice the rise and fall of your chest or abdomen
- Feel the air moving through your nostrils

When Mind Wanders:
- Notice when your attention drifts
- Gently return focus to your breath
- Avoid judging yourself for getting distracted

Close the Practice:
- Gradually expand your awareness
- Notice your surroundings
- Reflect on how your body and mind feel
Different Variations to Try

- Breath Counting: Count each breath to help focus the mind
- Deep Breathing (Diaphragmatic):Focus on belly breathing and helps deactivate stress response
- 4-7-8 Breathing:
- Inhale for 4 seconds
- Hold for 7 seconds
- Exhale for 8 seconds
- Particularly helpful for anxiety and sleep
- Box Breathing:
- Equal counts for inhaling
- Holding
- Exhaling
- Holding again
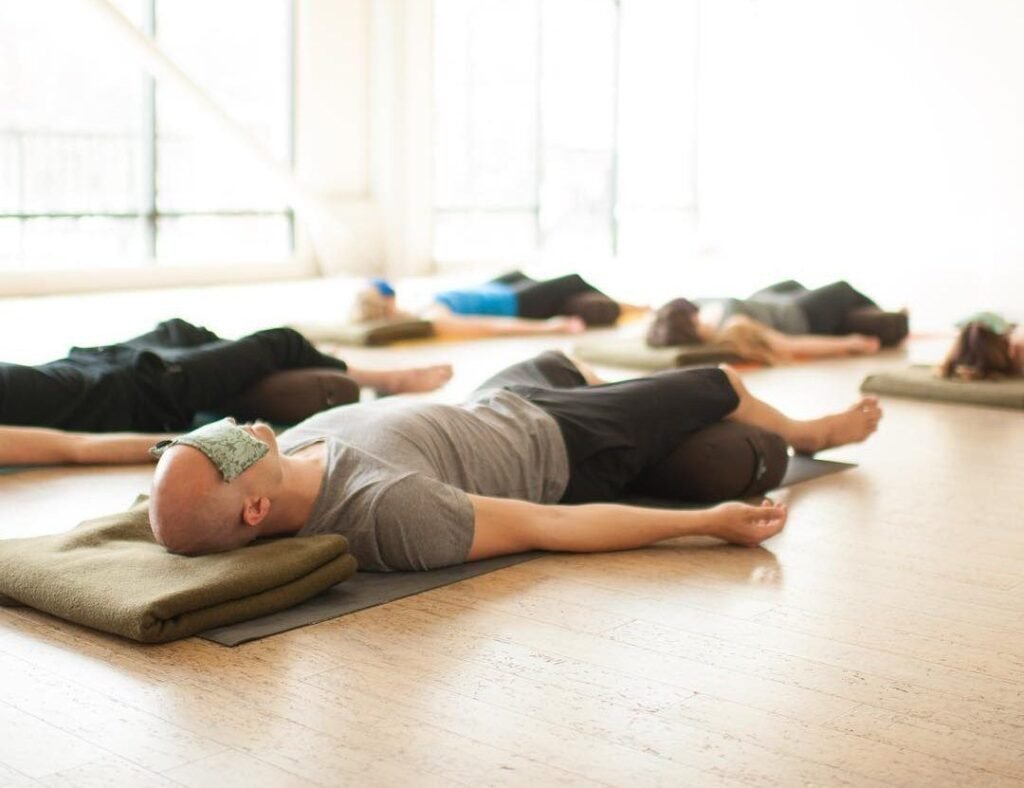
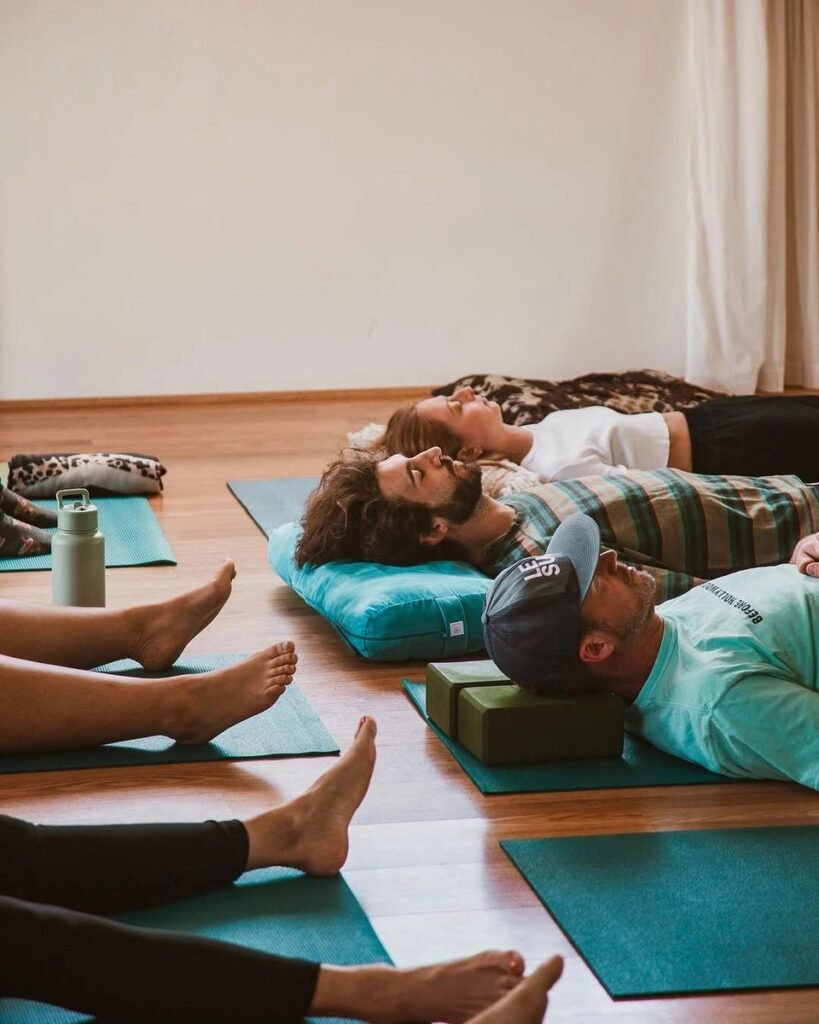
5. Yoga Nidra

Also known as “yogic sleep,” this type of meditation combines various methods of relaxation techniques. It’s particularly effective for those who struggle with anxious thoughts at bedtime or experience panic attacks .
The best way to practice Yoga Nidra is to use videos or online guided Yoga Nidra script or go to a Nidra class in a Yoga studio

Step-by-Step Practice Guide
1. Preparation
Create the Right Environment:
- Choose a quiet, dark roomEnsure comfortable temperature
- Use props like blankets or eye masks if needed
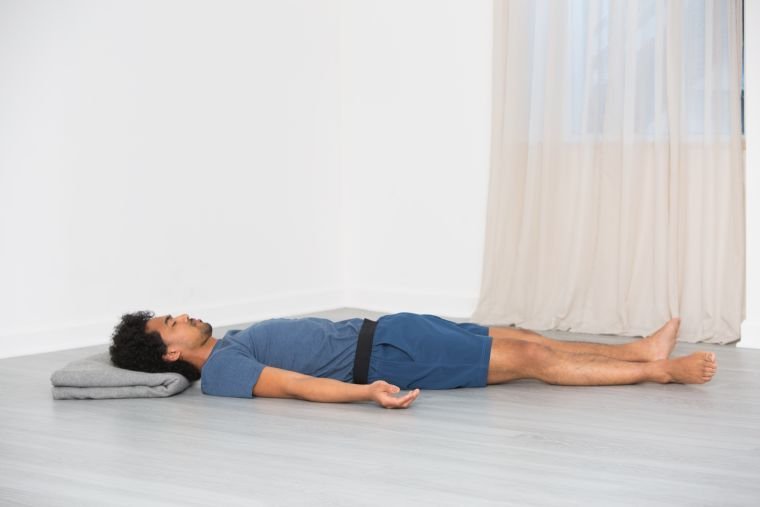

Find a Comfortable Position:
- Lie flat on your back in Shavasana (corpse pose)
- Place arms at sides, palms facing up
- Use pillows or blankets for support
2. The Practice

Initial Relaxation:
- Close your eyes gently
- Take deep breaths
- Count to 10 for each breath
Set Your Intention (Sankalpa):
- Choose a positive affirmation
- State it in present tense
- Keep it simple and clear
Body Scan Rotation:
- Follow systematic awareness through body parts
- Mentally name each part
- Release tension progressively
Breath Awareness:
- Observe natural breathing pattern
- Notice the rise and fall of abdomen
- Stay present with each breath
Visualization and Chakra Awareness:
- Focus on energy centers
- Visualize specific symbols or colors
- Connect with deeper consciousness
Completion:
- Reaffirm your initial intention
- Gradually return to awareness
- Slowly move fingers and toes
- Take deep breaths before opening eyes
Common Challenges and Solutions

Mental Distractions:
- Acknowledge wandering thoughts
- Gently return to practice
- Use guided sessions initially
Physical Discomfort:
- Use additional props for support
- Adjust position as needed
- Start with shorter sessions
Falling Asleep:
- Practice at times when you’re alert
- Maintain gentle awareness
- Use guided recordings
Recommended Resources and Tools
Apps:
- Insight Timer
- Yoga Nidra: Relax & Meditate
- Yoga Nidra: Sacred Sleep
Online Resources:
- Yoga Nidra Network
- Free guided sessions
- NSDR Protocols
Making Meditation Part of Your Daily Life
Creating a Sustainable Practice

To make meditation a successful part of your daily routine, consider these practical tips:
- Choose the Right Time of Day: Many meditation teachers recommend practicing in the morning before your to-do list takes over.
- Start Small: Begin with 5-10 minutes of meditation and gradually increase duration as you become more comfortable.
- Use Helpful Tools: Consider using a free meditation app like Insight Timer or other unguided meditations to support your practice.
- Create Your Space: Designate a quiet place for your practice, perhaps enhanced with essential oils or other elements that promote relaxation.
Understanding Different Ways to Practice

There are various forms of meditation available, including:
- Hatha yoga
- Tai Chi
- Transcendental meditation
- Mindfulness practice
- Guided visualization
Each offers unique benefits for mental health conditions and can be adapted to individual needs.
The Scientific Support

Recent clinical trials have shown significant differences in anxiety levels between those who meditate and control groups. A comprehensive review of 36 randomized controlled trials found that meditative therapies have a statistically significant effect in reducing anxiety symptoms.
When to Seek Professional Help

While meditation is a powerful tool for managing anxiety disorders, it’s important to recognize when to seek professional help. If you experience severe symptoms of anxiety or frequent panic attacks, consider combining meditation with other forms of treatment under professional guidance.
Meditation offers a scientifically-validated approach to managing anxiety through various methods. Whether you choose mindfulness meditation, body scan meditation, or other relaxation practices, the key to success lies in regular practice and finding the technique that resonates best with you.

Remember, the journey to inner peace and mental well-being is highly personal. Through direct experience and consistent practice, you can develop these mental health techniques into powerful tools for managing anxiety in your daily life.
[Note: This article contains health information based on scientific research and clinical trials. However, it should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare providers for personalized treatment plans.]

