Best 10 Mindfulness Practices and Tips to Improve Life
In our fast-paced world, finding inner peace and maintaining mental health has become more crucial than ever. Mindfulness, the practice of being fully present and engaged in the current moment, offers a powerful tool for navigating daily life with greater awareness and reduced stress. This comprehensive guide explores ten effective ways to incorporate mindfulness into your everyday life, backed by scientific research and expert recommendations.
1. Start Your Day with Mindful Breathing

Beginning your morning routine with mindful breathing sets a positive tone for the entire day. This simple practice involves taking slow breaths while paying close attention to physical sensations as air moves through your body . Research shows that regular practice of mindful breathing can effectively lower blood pressure and reduce stress levels.
How to Practice:
- Find a quiet place first thing in the morning
- Take 5-10 deep breaths
- Focus on the sensation of the air moving through your nostrils
- Notice how your body feels with each breath
- If your mind wanders, gently bring it back to your breathing
2. Transform Your Meals with Mindful Eating

Mindful eating is a great way to practice mindfulness while nourishing your body. This practice involves giving your full attention to the experience of eating, which can enhance digestion and promote better eating habits.
Mindful Eating Tips:
- Remove distractions (especially social media)
- Take time to appreciate the colors and aromas of your food
- Chew slowly and savor each bite
- Notice the textures and flavors
- Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues
3. Incorporate Mindful Walking into Your Daily Routine

Walking meditation offers a simple yet effective method to practice mindfulness, especially for those with busy schedules . Whether during your lunch break or commute, mindful walking can help you stay present while moving through your day.
Practice Guide:
- Choose a specific time for your walk
- Focus on each step
- Notice how your feet connect with the ground
- Observe your surroundings without judgment
- Pay attention to your body language and posture
4. Practice Digital Mindfulness

In our digital world, mindful technology use has become essential for maintaining mental health. Studies show that conscious engagement with digital devices can help reduce stress and improve focus.
Digital Mindful Strategies:
- Schedule regular digital detox periods
- Practice active listening during phone calls
- Set aside specific times for checking social media
- Create tech-free zones in your home
- Use mindfulness tools and apps mindfully
5. Implement Body Scan Meditation
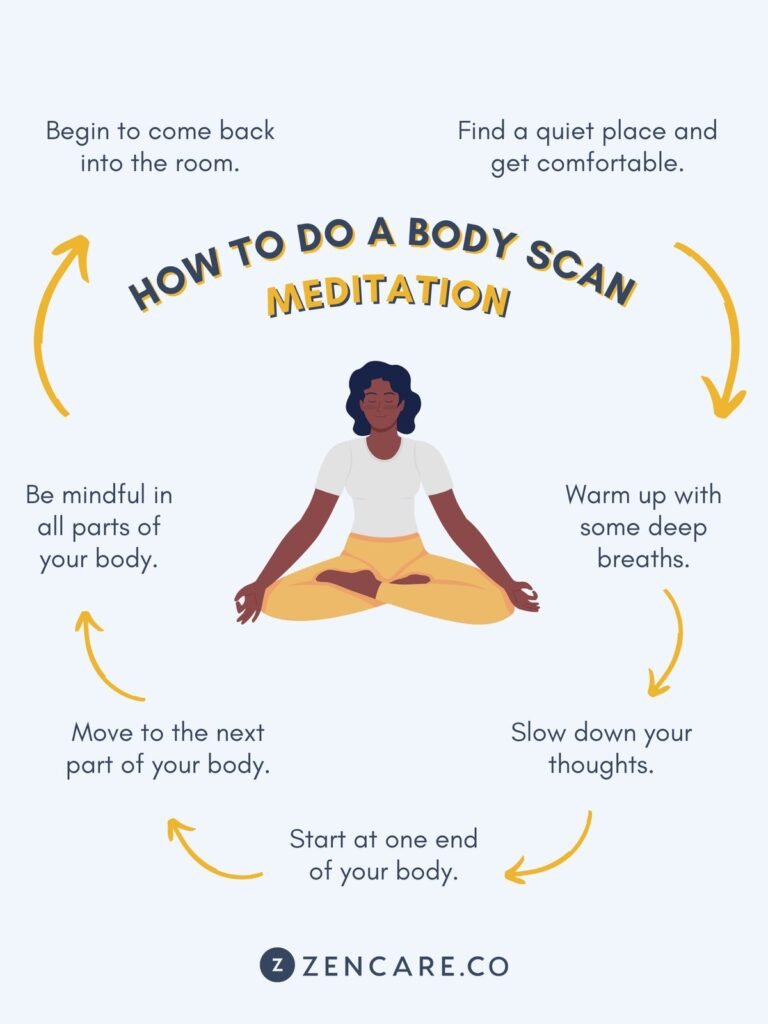
Body scan meditation is a powerful practice that can help reduce chronic pain and promote physical health . This technique involves progressive muscle relaxation and developing mindful awareness of different body sensations.
Steps for Body Scanning:
- Find a safe space and comfortable position
- Start from your toes and work up to your head
- Notice each muscle group without trying to change anything
- Observe any tension or discomfort
- Practice for 10-15 minutes daily
6. Cultivate Loving-Kindness Meditation

Loving-kindness meditation is a powerful tool for emotional health and building stronger connections with family members and close friends. This practice helps develop compassion and reduce negative thoughts.
Practice Guidelines:
- Begin with self-compassion
- Extend positive wishes to loved ones
- Gradually include neutral people and even difficult relationships
- Use simple phrases of goodwill
- Practice for 10-15 minutes daily
7. Engage in Mindful Listening
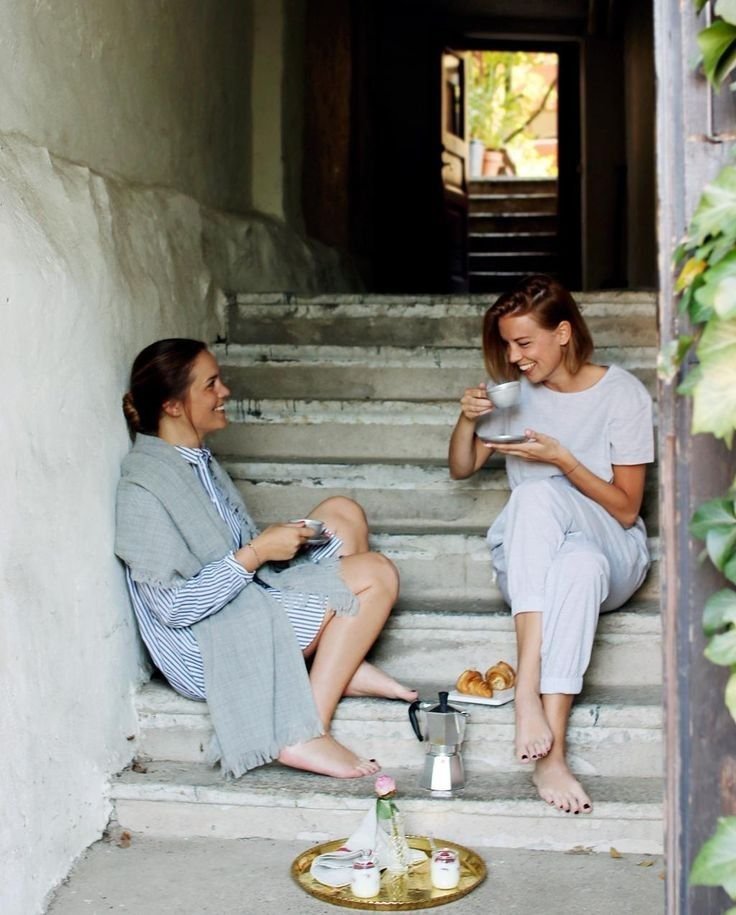

Mindful listening involves giving your undivided attention to sounds and conversations. This practice can improve relationships and communication while reducing stress.
How to Practice:
Focus completely on the speaker
Notice their body language
Avoid planning your response while others speak
Practice active listening in meetings
Pay attention to environmental sounds
8. Incorporate Gratitude Journaling
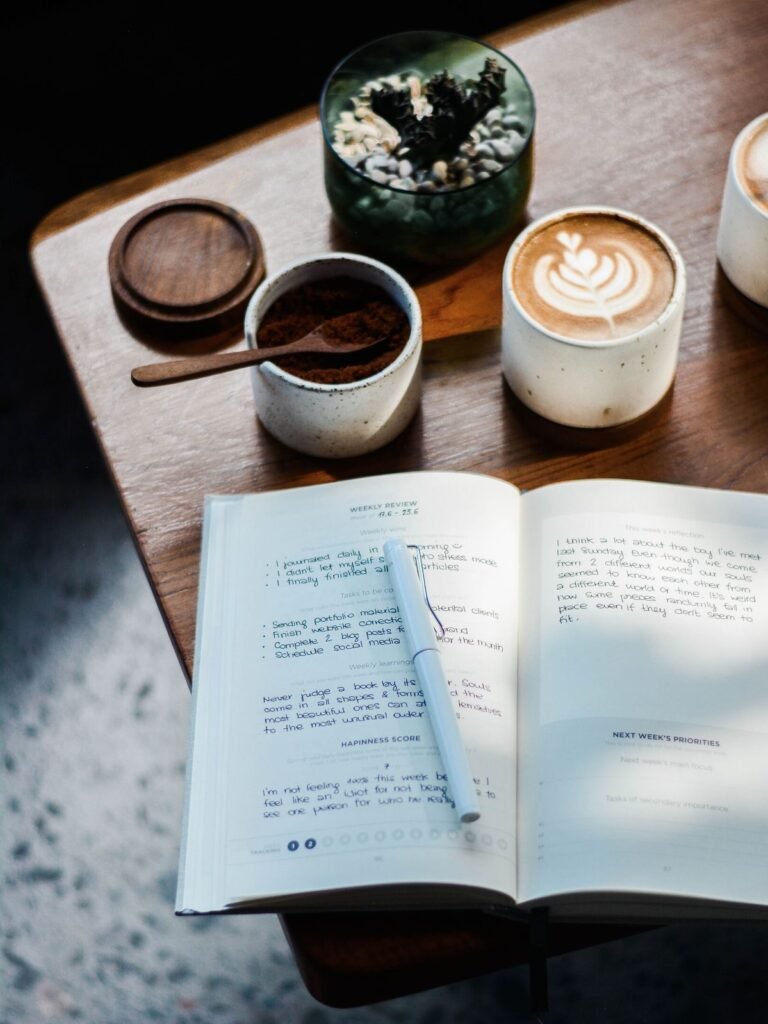

Combining mindfulness with gratitude journaling can have a positive impact on mental health and overall well-being. Clinical trials have shown that practicing gratitude can significantly improve emotional health.
Journaling Guidelines:
- Set aside time daily for reflection
- Write detailed gratitude lists
- Notice interesting things throughout your day
- Focus on the bigger picture
- Include both small and significant experiences
9. Practice Short Mindful Breaks

Even with busy schedules, taking short breaks for mindful can be an effective way to maintain present-moment awareness throughout the day.
Quick Mindful Exercises:
- Take three conscious breaths between tasks
- Perform simple mindfulness exercises during breaks
- Use everyday activities as mindful reminders
- Practice at your desk or in a quiet place
- Set regular mindful breaks in your to-do list
10. End Your Day Mindfully

Creating a mindful evening routine can help you transition from the state of alert to peaceful rest, improving sleep quality and overall wellness.
Evening Mindfulness Practices:
- Review your day without judgment
- Practice gentle breathing techniques
- Perform a brief body scan
- Express gratitude for the day
- Create a peaceful bedtime routine
What is Mindfulness Meditation?

Mindful meditation is a mental training practice that emphasizes being fully present and aware of your thoughts, feelings, and physical sensations without judgment. This practice encourages you to observe your experiences with curiosity and kindness, using your breath as an anchor to maintain focus on the present moment. It is rooted in ancient Buddhist traditions but has been adapted into a secular practice that is widely used today for its numerous mental health benefits, including stress reduction, improved emotional regulation, and enhanced overall well-being.
Benefits of Mindfulness Meditation

Engaging in mindful meditation can lead to a variety of positive outcomes, such as:
Reduced Stress: By focusing on the present moment, you can lower stress levels and cultivate a sense of calm .
Improved Focus: Regular practice helps train your mind to concentrate better, reducing distractions and enhancing productivity.
Emotional Health: Mindfulness meditation can help you manage negative thoughts and emotions, promoting a more positive mental state.
Enhanced Self-Awareness: This practice encourages a deeper understanding of your thoughts and feelings, fostering personal growth.
How to Practice Mindfulness Meditation

Practicing mindful meditation can be simple and accessible, even for beginners. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Set Aside Time and Find a Quiet Space
Choose a specific time each day to practice mindful meditation. This could be in the morning, during a lunch break, or before bed. Find a quiet place where you won’t be disturbed, allowing you to focus fully on your practice .
2. Get Comfortable
Sit in a comfortable position, either on a chair with your feet flat on the ground or on the floor with your legs crossed. You can also lie down if that feels more comfortable. Ensure your back is straight to promote alertness.
3. Close Your Eyes and Breathe
Gently close your eyes and take a few deep breaths. Inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to expand, and then exhale slowly through your mouth. Focus on the sensation of your breath entering and leaving your body.

4. Observe Your Thoughts and Sensations
As you settle into your practice, allow your thoughts to come and go without judgment. Notice any physical sensations in your body, such as tension or relaxation. If your mind wanders, gently bring your focus back to your breath .
5. Let Go of Judgments
It’s natural for thoughts and distractions to arise during meditation. Instead of trying to suppress them, acknowledge their presence and let them pass without attaching any judgment. This practice of non-attachment is key to developing mindful.
6. Practice Regularly
Aim to practice mindful meditation for at least 5-10 minutes each day. As you become more comfortable, you can gradually increase the duration of your sessions. Consistency is essential for reaping the benefits of mindful.
7. Incorporate Mindfulness into Daily Life
Beyond formal meditation, you can practice mindful throughout your day. Engage in everyday activities—like eating, walking, or even washing dishes—with full attention. Notice the sensations, sounds, and feelings associated with these tasks.

Where Does Mindfulness Come From?

Mindfulness, a practice that has gained immense popularity in recent decades, has its roots deeply embedded in ancient traditions, particularly Buddhism. While today it is widely recognized as a secular tool for improving mental health, reducing stress, and enhancing overall well-being, its origins are spiritual and philosophical. Understanding where mindfulness comes from requires exploring its historical, cultural, and linguistic roots, as well as its evolution into the modern practice embraced by millions worldwide.
The Origins of Mindfulness in Buddhism

The concept of mindfulness originates from the ancient Buddhist tradition, where it is referred to as “sati” in Pali, the language of many early Buddhist texts.
Sati is often translated as “awareness” or “recollection,” and it plays a central role in Buddhist teachings and meditation practices. In its original context, mindfulness was not merely about being present but also about cultivating a deep understanding of the nature of reality, including impermanence (anicca), suffering (dukkha), and the absence of a permanent self (anatta).

One of the foundational Buddhist texts on mindfulness is the Satipaṭṭhāna Sutta, which outlines the “Four Foundations of Mindfulness.” These foundations include mindfulness of the body, feelings, mind, and mental objects. The practice of mindfulness in this context involves observing these aspects of experience with non-judgmental awareness, allowing practitioners to develop insight into the nature of existence .
The Meaning of “Sati” and Its Translation
The term “sati” carries a nuanced meaning that goes beyond simple awareness. It encompasses the idea of remembering to stay present and attentive to the current moment. This remembrance is not about recalling past events but about maintaining a continuous awareness of what is happening in the present.

As Buddhist scholar John Peacock explains, sati involves “remembering to focus on what is otherwise too easily forgotten: the present moment”. The English word “mindfulness” was first used as a translation of sati by T.W. Rhys Davids, a prominent Buddhist scholar, in the early 20th century. Rhys Davids initially experimented with other translations, such as “mental activity” and “thought,” before settling on “mindfulness” in 1910.
This term was later popularized by Jon Kabat-Zinn, who developed the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program in the late 1970s. Kabat-Zinn defined mindfulness as “the awareness that arises through paying attention on purpose, in the present moment, and nonjudgmentally to the unfolding of experience moment by moment” .
Mindfulness in Other Traditions
While mindfulness is most closely associated with Buddhism, similar practices can be found in other spiritual and philosophical traditions. For example, in Hinduism, the practice of dhyana (meditation) involves focused attention and awareness, which parallels mindfulness meditation. In Taoism, the concept of living in harmony with the present moment aligns with the principles of mindfulness. Even in Western philosophy, thinkers like the Stoics emphasized the importance of being present and accepting what is beyond one’s control.
The Evolution of Mindfulness in the West

Mindfulness began to gain traction in the West during the 20th century, thanks to the efforts of Buddhist teachers and scholars who introduced these practices to a broader audience. Figures like Thích Nhất Hạnh, a Vietnamese Zen master, and Joseph Goldstein, a prominent meditation teacher, played key roles in spreading mindfulness teachings.

Their work emphasized the universal applicability of mindfulness, making it accessible to people of all backgrounds. The secularization of mindfulness was further advanced by Jon Kabat-Zinn, who integrated mindfulness into clinical settings through his MBSR program. This program was initially designed to help patients manage chronic pain but has since been applied to a wide range of psychological and physical health conditions. Kabat-Zinn’s work marked a turning point in the history of mindfulness, transforming it from a spiritual practice into a scientifically validated therapeutic tool .
Mindfulness in Modern Psychology and Medicine

Since the 1970s, mindfulness has been extensively studied in clinical psychology and psychiatry. Research has shown that mindfulness-based interventions can reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress, as well as improve overall mental health. These interventions, such as Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), have been particularly effective in preventing relapse in individuals with recurrent depression .Mindfulness has also been found to have significant physical health benefits. Studies suggest that mindfulness meditation can reduce inflammation, improve immune function, and even lower blood pressure. By reducing rumination and worry, mindfulness helps mitigate the physiological effects of stress, which can contribute to chronic health conditions .
Critiques and Challenges

Despite its widespread popularity, mindfulness has faced criticism, particularly regarding its commercialization and over-marketing. Critics argue that the essence of mindfulness has been diluted in its transition to the West, with some programs focusing more on productivity and stress reduction than on the deeper insights emphasized in traditional Buddhist teachings. Additionally, there is a need for more rigorous scientific studies to validate some of the claimed benefits of mindfulness .
Incorporating these practical ways to practice mindfulness into your daily lives doesn’t require much time – just commitment and regular practice. As supported by Harvard Health Publishing and numerous clinical trials, mindfulness is a powerful tool for improving both mental and physical health.
Remember that mindfulness is a journey, not a destination. Start with simple exercises that feel manageable, and gradually expand your practice as you become more comfortable. With consistent effort, these mindfulness techniques can transform your everyday life, leading to greater inner peace and well-being in our fast-paced world.

