Collagen Complete Guide : Benefits & Usage
Have you tried Collagen ? It is one of the most used supplement in the world . Good for the body, bones, skins, nails and overall for your general wellness. Please check our articles below with our full guide about how to use collagen in a smart way


Collagen, often referred to as the “glue” that holds our bodies together, is a fascinating and essential protein that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. As the most abundant protein in the human body, collagen is a key component of connective tissues, providing structural support to our skin, bones, muscles, and blood vessels. In recent years, collagen has gained significant attention in the wellness community, with many touting its potential benefits for skin health, joint function, and even gut health. This article will delve deep into the world of collagen, exploring its structure, functions, and the growing trend of collagen supplementation.
The Science Behind Collagen
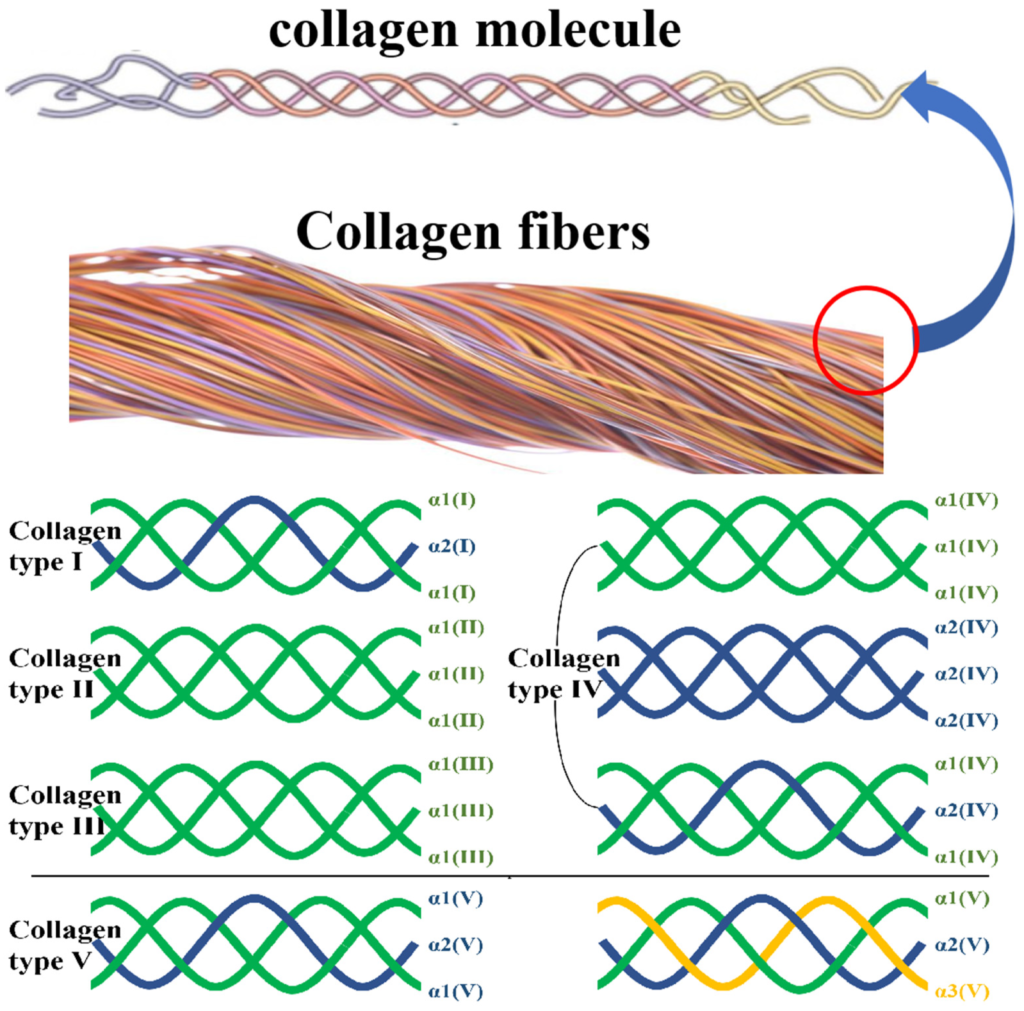
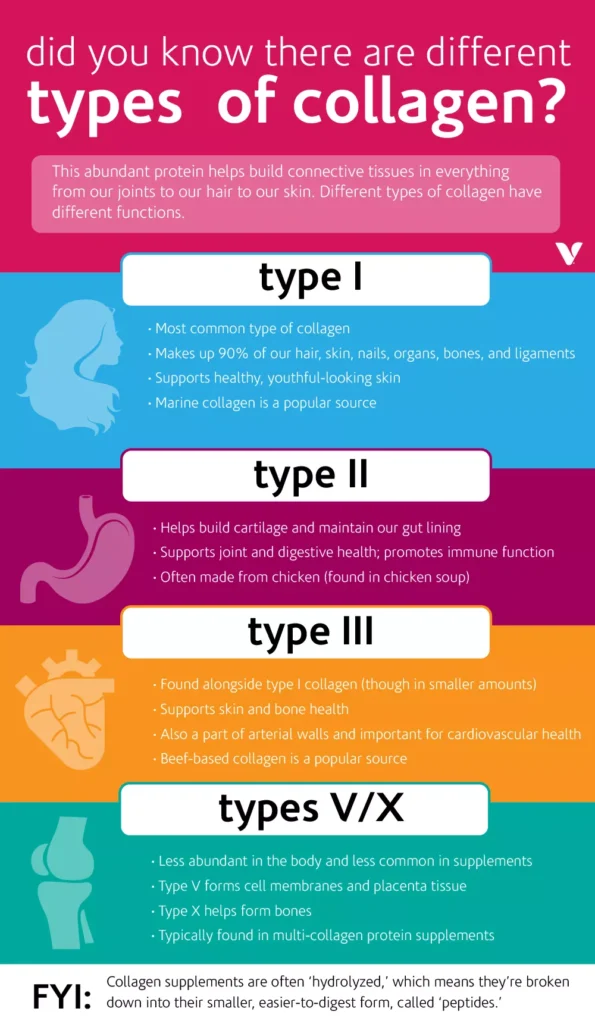
Collagen is a naturally occurring protein composed of amino acids, the building blocks of all proteins. What sets collagen apart is its unique triple-helix structure, which gives it remarkable strength and flexibility. This structure is formed by three polypeptide chains, each containing specific sequences of amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. The triple-helix structure of collagen, which gives it its unique properties.There are at least 28 different types of collagen identified in the human body, but types I through V are the most common and well-studied.
Each type of collagen has specific functions and is distributed differently throughout the body:
1. Type I Collagen: This is the most abundant type, making up about 90% of the body’s collagen. It provides structure to skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
2. Type II Collagen: Found primarily in cartilage, this type is crucial for joint health.
3. Type III Collagen: Works alongside Type I collagen in skin, muscles, and blood vessels.
4. Type IV Collagen: Essential for filtration, found in the basal lamina of various tissues.
5. Type V Collagen: Present in hair, cell surfaces, and the placenta.
The Importance of Collagen in the Human Body
Collagen plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions and structures:
Skin Health and Elasticity

Collagen is a key component of the dermis, the layer of skin responsible for its structure and elasticity. As we age, our bodies produce less collagen, leading to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines. Maintaining adequate collagen levels is crucial for preserving skin elasticity and promoting a youthful appearance.
Joint Health and Pain Relief
Type II collagen is a major component of cartilage, the tissue that cushions our joints. Adequate collagen levels can help maintain joint health and potentially alleviate joint pain, especially in conditions like osteoarthritis .
Bone Health and Density

Collagen provides the framework for bone mineralization. It helps maintain bone density and strength, which is particularly important for postmenopausal women who are at higher risk of osteoporosis .
Muscle Mass and Strength

Collagen is an essential component of muscle tissue, providing structural support and contributing to muscle strength and function .
Blood Vessel Integrity
Type III collagen is crucial for maintaining the integrity of blood vessels, supporting cardiovascular health .
Collagen Production and Natural Sources
Our bodies naturally produce collagen, but this production decreases as we age. Several factors can affect collagen synthesis:
Factors Affecting Collagen Production
- Age: Collagen production naturally declines with age.
- UV Exposure: Excessive sun exposure can degrade collagen fibers.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can impair collagen production and accelerate its breakdown.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for collagen synthesis.
Natural Sources of Collagen
While the body can produce collagen, we can also obtain it from various food sources:

- Bone Broth: A rich source of collagen, made by simmering animal bones and connective tissues.
- Animal Products: Chicken skin, fish, and beef are excellent sources of collagen.
- Egg Whites: While not containing collagen directly, they are rich in proline, an amino acid crucial for collagen production.
Boosting Collagen Production Naturally
Several nutrients and lifestyle factors can support natural collagen production:

1. Vitamin C: Essential for collagen synthesis, found abundantly in citrus fruits and leafy greens
2. Protein-Rich Foods: Provide the amino acids necessary for collagen production.
3. Antioxidants: Help protect existing collagen from damage caused by free radicals.
4. Hydration: Adequate water intake supports overall skin health and collagen function.
Collagen Supplementation: Forms and Benefits
The growing interest in collagen’s potential health benefits has led to a surge in collagen supplementation. These supplements come in various forms:
Types of Collagen Supplements

Collagen Powder: Often hydrolyzed for better absorption, easily mixed into beverages.
Liquid Collagen: Pre-dissolved form, claiming higher bioavailability.
Collagen Peptides: Highly bioavailable form, broken down into smaller peptide chains.
The process of collagen biosynthesis in the body.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Collagen
1. Skin Health and Anti-Aging Properties

Collagen is a key component of the dermis, the layer of skin responsible for its structure and elasticity. As we age, our bodies produce less collagen, leading to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines . Collagen supplementation has shown promising results in improving skin health:
Enhanced Skin Elasticity: Studies have demonstrated that oral collagen supplements can significantly improve skin elasticity and hydration, reducing the appearance of wrinkles .
Increased Skin Hydration: Collagen peptides have been found to increase skin moisture content, contributing to a more youthful appearance .
Protection Against UV Damage: Some research suggests that collagen may help protect the skin from harmful UV rays, potentially reducing the risk of photoaging .
2. Joint Health and Pain Relief

Type II collagen is a major component of cartilage, the tissue that cushions our joints. Collagen supplementation has shown potential benefits for joint health:
Reduced Joint Pain: Studies have found that collagen supplements can help alleviate joint pain, particularly in individuals with osteoarthritis .
Improved Joint Function: Regular intake of collagen peptides may enhance joint mobility and reduce stiffness, especially in athletes and active individuals .
Cartilage Regeneration: Some research suggests that collagen supplementation may support cartilage regeneration, potentially slowing the progression of joint degeneration .
3. Bone Health and Density

Collagen provides the framework for bone mineralization, contributing to bone strength and density. This is particularly important for postmenopausal women, who are at higher risk of osteoporosis:
Increased Bone Mineral Density: A study involving postmenopausal women found that those who took collagen supplements showed significant increases in bone mineral density compared to those who did not.
Reduced Risk of Bone Disorders: Regular collagen intake may help reduce the risk of bone disorders and fractures, especially in older adults .
4. Muscle Mass and Strength

Collagen is an essential component of muscle tissue, providing structural support and contributing to muscle strength and function:
Enhanced Muscle Mass: Some studies suggest that collagen supplementation, when combined with resistance training, may help improve muscle mass and strength, particularly in older adults .
Faster Recovery: Collagen may aid in muscle recovery after intense exercise, potentially reducing muscle soreness and improving performance .
5. Gut Health

Emerging research suggests that collagen may play a role in supporting gut health:
Improved Intestinal Barrier Function: Collagen contains amino acids that may help strengthen the intestinal lining, potentially reducing gut permeability and associated issues .
Digestive Comfort: Some individuals report improved digestive comfort when supplementing with collagen, though more research is needed to confirm these effects .
Sources of Collagen and Boosting Production
Natural Sources of Collagen
While our bodies produce collagen naturally, we can also obtain it from various food sources:

1. Bone Broth: A rich source of collagen, made by simmering animal bones and connective tissues .
2. Animal Products: Chicken skin, fish, and beef are excellent sources of collagen .
3. Egg Whites: While not containing collagen directly, they are rich in proline, an amino acid crucial for collagen production.
Boosting Collagen Production Naturally

Several nutrients and lifestyle factors can support natural collagen production:
1. Vitamin C: Essential for collagen synthesis, found abundantly in citrus fruits and leafy greens.
2. Protein-Rich Foods: Provide the amino acids necessary for collagen production.
3. Antioxidants: Help protect existing collagen from damage caused by free radicals.
4. Hydration: Adequate water intake supports overall skin health and collagen function.
Collagen Types Beneficial for Skin Health

When it comes to skin health, not all collagen types are created equal. The research indicates that certain types of collagen are particularly beneficial for maintaining skin structure, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Type I Collagen: The Primary Skin Collagen

Type I collagen is overwhelmingly the most important type for skin health. It is the most abundant collagen in the human body and plays a crucial role in maintaining skin structure and appearance.
Here’s why Type I collagen is so beneficial for the skin:
1. Structural Support: Type I collagen provides the primary structural support for the skin, forming a network of fibers that give the skin its firmness and strength.
2. Elasticity: It contributes significantly to skin elasticity, which is essential for maintaining a youthful appearance and preventing sagging.
3. Wrinkle Reduction: By supporting the skin’s structure, Type I collagen helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.

Type III Collagen: The Youth-Associated Collagen
Type III collagen is often found alongside Type I collagen in the skin, particularly in younger individuals. It plays a significant role in skin elasticity and firmness. As we age, the production of Type III collagen decreases, which contributes to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin. Supplementing with Type III collagen can potentially help maintain a more youthful skin appearance.
Type IV Collagen: The Skin Barrier Supporter
While not as abundant as Types I and III, Type IV collagen is crucial for skin health. It is a key component of the basement membrane zone, which separates the epidermis from the dermis. This type of collagen provides structural support and acts as a barrier, playing a vital role in maintaining skin integrity and function.
How to Use Collagen for Skin Health
Now that we’ve identified the most beneficial collagen types for skin health, let’s explore how to use collagen effectively to maximize its benefits.
1. Oral Supplementation
Oral collagen supplements are the most common and effective way to boost collagen levels for skin health. Here’s how to use them:
Form: Hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides) is the most bioavailable form, making it easier for the body to absorb and utilize.
Dosage: For skin health, a daily intake of 2.5 to 5 grams of hydrolyzed collagen is typically recommended
Timing: While consistency is more important than exact timing, taking collagen in the morning can be beneficial for maximizing absorption and benefits throughout the day.
Duration: Regular daily intake is crucial. Most studies show benefits after 4-12 weeks of consistent use.
2. Choosing the Right Supplement Form
Collagen supplements come in various forms, each with its own advantages:
Powders: Highly versatile and can be easily mixed into beverages or foods. They typically have good bioavailability and are a popular choice for daily use .
Liquid Collagen: Offers the highest bioavailability, with absorption rates reported to be as high as 90-95% . This makes it an excellent choice for those seeking quick results, particularly for skin hydration and elasticity.
Pills and Capsules: While convenient, they may have lower bioavailability compared to powders and liquids, with an absorption rate of around 40-45% .
3. Enhancing Collagen Absorption
To maximize the benefits of collagen supplementation for skin health:
Combine with Vitamin C: Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis. Consuming vitamin C-rich foods or supplements alongside collagen can enhance its effectiveness .
Maintain a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in protein, zinc, and copper supports natural collagen production in the body.
Avoid Collagen Destroyers: Minimize exposure to factors that break down collagen, such as excessive sun exposure, smoking, and high sugar intake.
4. Topical Application
While oral supplementation is generally more effective, some people also use topical collagen products:
Effectiveness: The effectiveness of topical collagen is limited because collagen molecules are typically too large to penetrate the skin barrier effectively .
Supporting Ingredients: Look for topical products that combine collagen with other beneficial ingredients like hyaluronic acid or retinoids, which can improve overall skin appearance.
5. Lifestyle Factors
In addition to supplementation, certain lifestyle factors can support collagen production and skin health:
Sun Protection: Use sunscreen daily to protect collagen from UV damage.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep skin hydrated and support overall skin health.
Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for skin repair and collagen production.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve circulation, which supports skin health and collagen production.
Quality Considerations and Safety
When choosing a collagen supplement for skin health, consider the following:
Source: Marine collagen (Type I) is often preferred for its lower risk of contamination and inflammation.
Third-Party Testing: Look for supplements that have been tested by independent organizations to ensure purity and safety.
Allergies: Be aware of potential allergies, especially if using marine-sourced collagen.
Consultation: Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Conclusion
Type I collagen, followed by Types III and IV, are the most beneficial for skin health. To use collagen effectively for skin benefits, opt for hydrolyzed collagen supplements in powder or liquid form, aiming for a daily intake of 2.5 to 5 grams. Enhance absorption by combining with vitamin C and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While topical applications have limited effectiveness, they can be used in conjunction with oral supplements for a comprehensive approach to skin care.
Remember that consistency is key, and visible improvements typically require several weeks of regular use. By choosing high-quality supplements and following these guidelines, you can maximize the potential skin benefits of collagen supplementation.