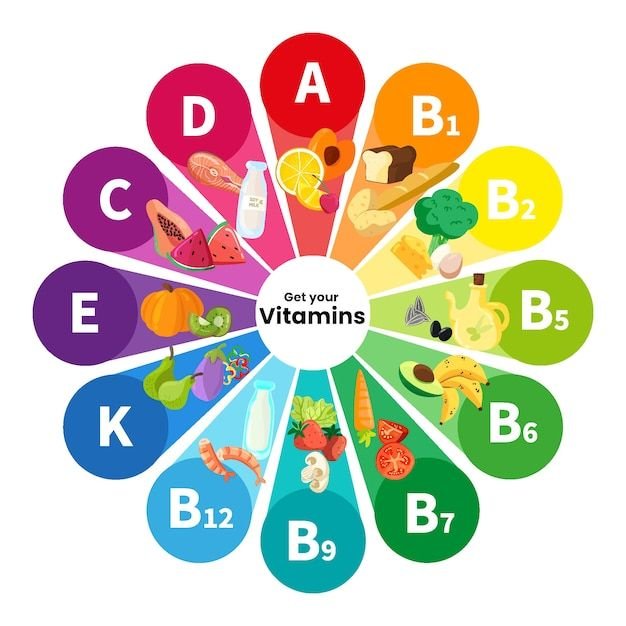
Don’t Miss Out! The 6 Vitamins for Daily Wellness

In our quest for wellness, understanding the essential vitamins our bodies need is crucial. This comprehensive guide will explore the vital nutrients that play an important role in maintaining good health, from fat-soluble vitamins to water-soluble vitamins, and how to incorporate them into your daily diet. Whether you’re following a vegan diet or simply looking to optimize your nutritional intake, this article will provide you with the knowledge to become a true Wellness Warrior.
Understanding Vitamins: The Building Blocks of Health

Vitamins are essential nutrients that our bodies require in small amounts to function properly. They play a crucial role in various bodily processes, from supporting our immune system to maintaining strong bones and a healthy heart. Vitamins are classified into two main categories: fat-soluble vitamins and water soluble vitamins.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins

Fat-soluble vitamins include Vitamins A, D, E, and K. These vitamins are absorbed along with dietary fats and can be stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. Because they can be stored, they don’t need to be consumed as frequently as water-soluble vitamins. However, it’s important to note that excessive intake of fat-soluble vitamins can lead to toxicity .
Water-Soluble Vitamins
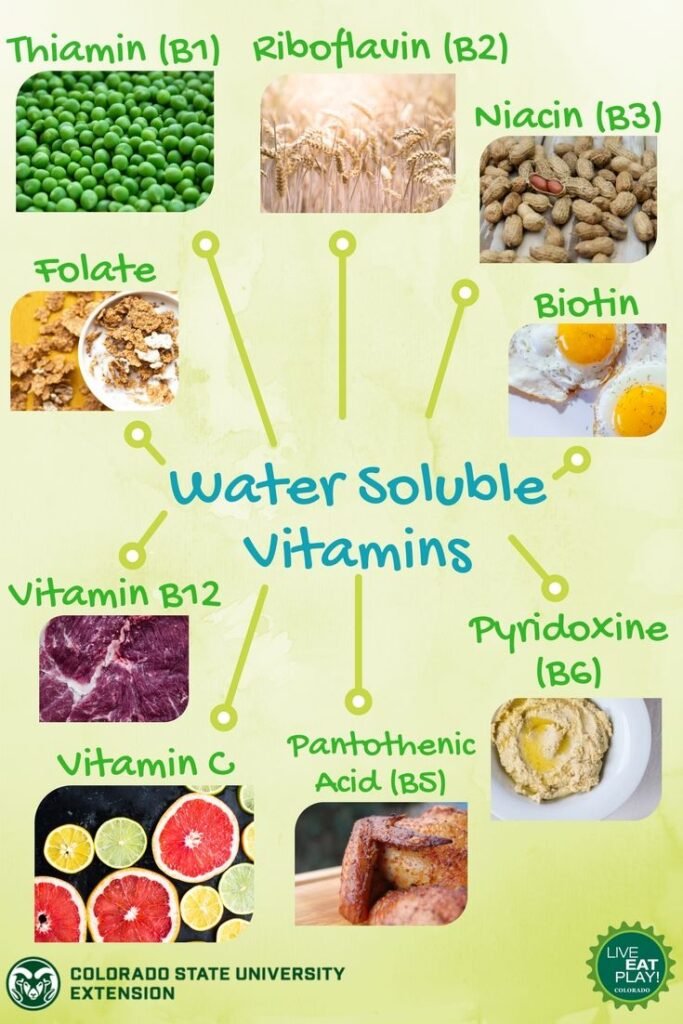
Water-soluble vitamins include the B-complex vitamins and Vitamin C. These vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored in the body, which means they need to be consumed more regularly. Excess amounts are typically excreted in urine, reducing the risk of toxicity.
Risks of vitamins deficiency
Vitamin deficiencies pose significant risks to the human body, potentially leading to a range of serious health complications and long-term effects.
These deficiencies can impact various bodily systems, from neurological function to bone health, and even increase the risk of certain chronic diseases. For instance, a lack of vitamin B12 can result in neurological problems such as vision issues, memory loss, and peripheral neuropathy, which may become irreversible if left untreated.
Folate (vitamin B9) deficiency is particularly dangerous during pregnancy, as it can lead to severe birth defects like spina bifida and anencephaly.
Vitamin D deficiency primarily affects bone health, contributing to conditions like rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, while also increasing the risk of fractures and certain chronic diseases. Vitamin A deficiency can cause vision problems, including night blindness and xerophthalmia, which may progress to complete blindness if not addressed.
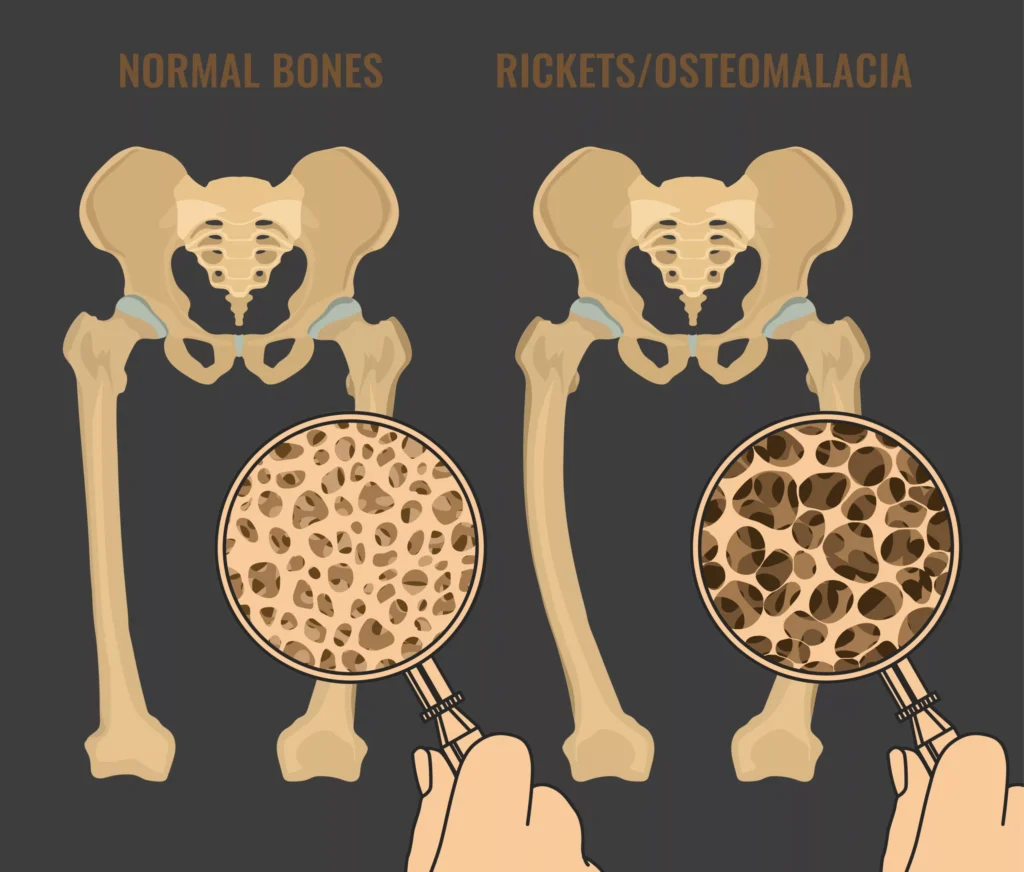
It also impairs immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections. Severe vitamin C deficiency can lead to scurvy, characterized by bleeding gums, joint pain, and anemia. These deficiencies are often preventable through a balanced diet and, when necessary, appropriate supplementation. However, certain populations are at higher risk, including the elderly, pregnant women, vegans, and individuals with specific health conditions.
Regular monitoring and targeted interventions are crucial to prevent these deficiencies and their associated health risks, ensuring optimal bodily function and overall well-being.
READ MORE: Lists for Daily Minerals You Should Take!
Essential Vitamins for Daily Intake
1. Vitamin A

Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function. It plays a vital role in cell growth and differentiation, which is essential for the development and maintenance of healthy organs such as the heart, lungs, and kidneys.
Food Sources: Beef liver, eggs, dairy products, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, and mangoes.
Vegan Options: Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and mangoes.
2. B Vitamins

The B-complex vitamins include eight different vitamins: B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin). These vitamins are crucial for energy production, brain function, and cell metabolism.
Food Sources: Whole grains, lean meats, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Vegan Options: Fortified cereals, nutritional yeast, and plant-based milks for B12.
3. Vitamin C

Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage by free radicals. It is essential for the synthesis of collagen, which is important for skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels.
Food Sources: Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.
4. Vitamin D

Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D is crucial for bone health as it helps the body absorb calcium.
It also plays a role in immune function and reducing inflammation.
Food Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks.
Vegan Options: Fortified plant-based milks, fortified cereals, and mushrooms exposed to UV light.
5. Vitamin E

Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. It is important for
immune function and skin health.
Food Sources: Vegetable oils, leafy green vegetables, whole grains, and nuts .
Vegan Options: Sunflower seeds, almonds, and spinach.
6. Vitamin K

Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone metabolism. It helps in the synthesis of proteins required for blood coagulation and bone health.
Food Sources: Leafy green vegetables like kale, spinach, and broccoli.
READ MORE: Benefit Taking Collagen Daily for Health
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
While understanding individual vitamins is crucial, it’s equally important to recognize that a well-balanced
diet is the best way to ensure adequate intake of these essential nutrients. A varied diet rich in fruits,
vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and dairy products can provide most of the vitamins and minerals
needed for good health.

For those following a vegan or plant-based diet, special attention should be paid to certain nutrients, particularly vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products. Fortified foods and dietary supplements can help bridge any nutritional gaps.
Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs)
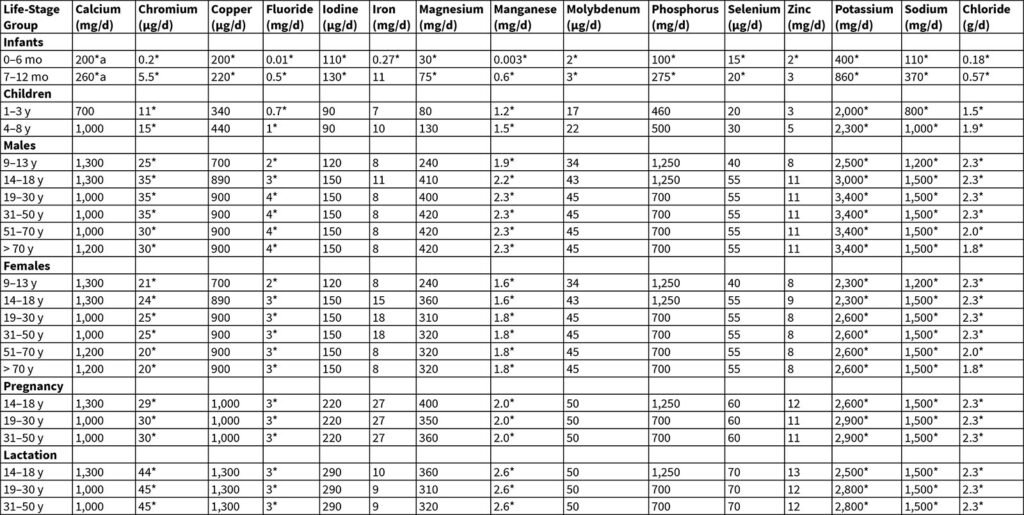
The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) provide guidelines for the average daily intake of nutrients sufficient to meet the needs of nearly all healthy individuals. These values vary by age, sex, and life stage, including considerations for pregnant and lactating women. For example:
● Vitamin C: Adult men need 90 mg per day, while adult women need 75 mg per day.
● Vitamin D: Adults (19-70 years) require 600 International Units (IU) per day.
● Calcium: Adults (19-50 years) need 1,000 mg per day.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the right amount of vitamins for your individual needs, especially if you have specific health conditions or dietary restrictions.
The Role of Dietary Supplements

While a healthy diet should be the primary source of vitamins and minerals, dietary supplements can play an important role in filling nutritional gaps. The prevalence of supplement use in the United States is significant, with 57.6% of adults aged 20 and over reporting the use of dietary supplements in the past 30 days during 2017–2018.
However, it’s crucial to note that supplements are not a substitute for a balanced diet. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not review dietary supplements for safety and effectiveness before they are marketed, which can lead to potential risks if supplements are not used properly.
Special Considerations for Different Groups
1. Pregnant Women

Pregnant women have increased nutritional needs to support both their health and the development of the fetus. Folic acid, in particular, is crucial for preventing birth defects like spina bifida. Prenatal vitamins are often recommended to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients .
2. Older Adults

As people age, their nutritional needs change. Older adults may require more vitamin D and calcium to maintain bone health, as well as vitamin B12, which is crucial for brain function and red blood cell formation.
3. People with Specific Health Conditions

Individuals with chronic conditions such as heart disease or diabetes may have unique dietary requirements. It’s essential for those with health conditions to consult with healthcare providers before starting any new supplement regimen, as certain vitamins and supplements can interact with medications.
The Impact of Vitamins on Overall Health
Adequate vitamin intake is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing various medical conditions. For instance:
● Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular
diseases, and certain cancers.
● B vitamins play a vital role in energy production and brain function, with deficiencies potentially
leading to anemia and cognitive impairments.
● Antioxidant vitamins like C and E help protect against oxidative stress, which is associated with
various chronic diseases.
Conclusion: Becoming a Wellness Warrior
As we’ve explored, vitamins play an essential role in human health, supporting everything from our
immune system to our heart health. By understanding the importance of these vital nutrients and
incorporating them into our daily diet through a combination of healthy foods and, when necessary,
dietary supplements, we can take significant steps towards optimal health.
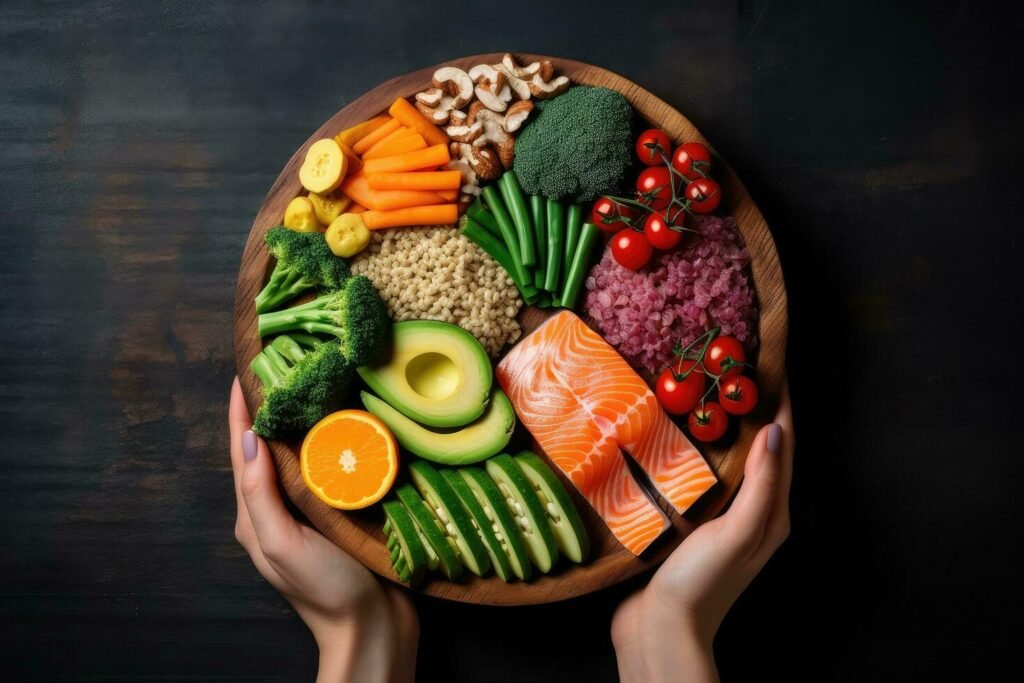

Remember, the key to becoming a true Wellness Warrior lies in maintaining a balanced approach. Focus on consuming a varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Pay attention to your body’s needs and consult with healthcare providers to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional requirements.
By arming yourself with knowledge about essential vitamins and making informed choices about your diet and supplement use, you’re well on your way to nourishing your body and achieving lasting wellness.
Here’s to your health, Wellness Warriors!